Graduate School of Science and Engineering Information and Computer Science
- Course Outline
- Laboratory for Information Theory and its Applications
- Information Systems Laboratory
- Intelligent Information Processing Laboratory
- Intelligent Mechanism Laboratory
- Intelligent Systems Design Laboratory
- Socio-informatics Laboratory
- Co-Creation Informatics Laboratory
- Applied Media Information Laboratory
- Network Information Systems Laboratory
- Intelligent Mechatro-Informatics Laboratory
- Spoken Language Processing Laboratory
Information Systems Laboratory
Research and development of computer application to non-IT area
Staff
[Professor]
| Acceptable course | |
|---|---|
| Master's degree course | |
| Doctoral degree course | |
Telephone :
Office :
Research Topics
- Multi-agent simulations
- Application of the blockchain technology as a highly reliable and secure database
- ***ing paintings by computing
Research Contents
Our research group focuses on the application of information technology to wide range of fields. Major research fields are shown below.
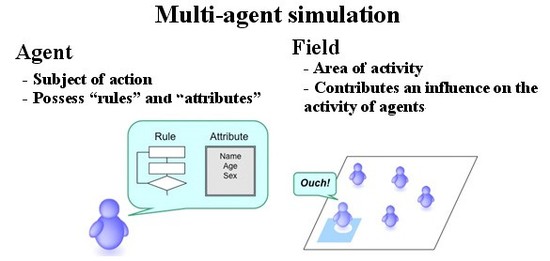
<1> Multi-agent simulation (MAS) research:
In MAS, execution subjects called agents mutually interact, and through the process of changes in their statuses,
you can view in what way a macro (artificial society) as the micro (agent) aggregate changes its structure. The
analysis of this micro (agent) and macro (artificial society) loop (Micro-Macro Loop) is one of the central issues
of MAS. People are normally interested in the effect (emergence) from micro to macro, but in our laboratory, we
are conversely aware of the problem; "what kind of interactions at the micro level are necessary to make the
desired macro phenomena emerge?" For this issue, the major issues are developing and implementing simulation
models in the field of ITS (Intelligent Transportation System) and discovering dominant factors from there. The
simulation of the ITS is only one example of the simulation of social behavior. Another topic of our research
includes the electoral system of Japanese Diet member. More examples such as the direct computation of physical
phenomenon such as heat transfer and wave propagation can be simulated by MAS. MAS is a widely applicable
general-purpose methods. We will investigate wide range of application fields by using this technology.
<2> Application of the blockchain technology as a highly reliable and secure database:
Blockchain is one of the most up-to-date technology. Crypt-currency such as Bitcoin is one of the most famous
applications of blockchain technology. Some people often confuse blockchain technology with crypt-currency. But
the latter is just a specific application of the former. We consider the blockchain technology as a highly
reliable, secure database technology. A blockchain stores a growing set of records, each of which describes some
timestamped peer exchanges/transactions, stored in chronological order.
We will consider the blockchain technology as NOT the crypt-currency BUT the highly-reliable database. Based on this consideration, we will develop
various kinds of applications.
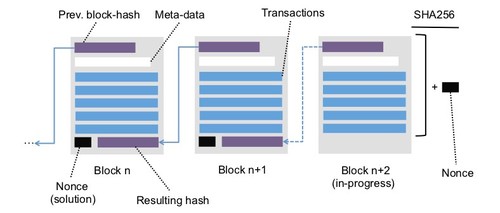
Conceptual illustration of blockchain.
<3>***ing paintings by
computing
The term “***ing” contains two words: “analyzing” and “synthesizing.”
- The first word “analyzing”
comes from (my) very simple and naive questions:
- Why great paintings are great?
- What, on earth, is abstract paintings?
We will try to approach to these two questions by using the research results of computer science and information technology such as image processing, machine learning, and wavelet transformation. Great paintings have an innovativity in the usage of coloring, recognizing figures, and combination of them. They receive less influence from precedent works and also have huge influence to the succeeding paintings. Therefore, if we could “measure” the similarity of two or more paintings, we will be able to construct the “influence graph of paintings.” By using this graph, we will try to assess the “degree of originality” of each painting.
- The second word “synthesizing” comes from the concept of “Generative Art.” Generative art is an art that in whole or in part has been created (generated) with the use of an autonomous system such as computers and algorithms. Some abstract paintings such as works of Piet Mondrian can be considered as an example of the generative art. By using the autonomous and randomness, we may be able to generate some abstract paintings. We will start from the following assumption of abstract paintings: Abstract painting is a result of reconstruction of color and figures extracted from concrete scene. By using this assumption, we will try to synthesize (generate) new location-aware abstract paintings.
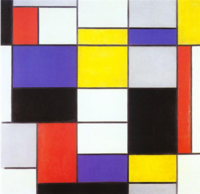
Work of Piet Mondrian

Generative Art generated
from Euclid’s Algorithm
Keywords
- Multi-agent
- Blockchain technology
- Art and Computing